Spring 中的 Bean 的概念
Bean的配置信息定义了Bean的实现及依赖关系,Spring容器根据各种形式的Bean配置信息在容器内部建立Bean定义注册表,然后根据注册表加载、实例化Bean,并建立Bean和Bean的依赖关系,最后将这些准备就绪的Bean放到Bean缓存池中,以供外层的应用程序进行调用。
Spring 中的 bean 的作用域
- singleton:唯一 bean 实例,Spring 中的 bean 默认都是单例的。
- prototype:每次请求都会创建一个新的 bean 实例。
- request:每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,该bean仅在当前HTTP request内有效。
- session:每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该bean仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效。
- application:作用于 ServletContext 的生命周期。
- websocket:作用于 WebSocket 的生命周期。
Spring 中的单例 bean 的线程安全问题
大部分时候我们并没有在系统中使用多线程,所以很少有人会关注这个问题。单例 bean 存在线程问题,主要是因为当多个线程操作同一个对象的时候,对这个对象的非静态成员变量的写操作会存在线程安全问题。 常见的有两种解决办法:
- 在Bean对象中尽量避免定义可变的成员变量(不太现实)。
- 在类中定义一个ThreadLocal成员变量,将需要的可变成员变量保存在 ThreadLocal 中(推荐的一种方式)。
Spring 中的 bean 生命周期
大致的生命周期可以分为:
- bean 的定义
- 在配置文件里面用
<bean></bean>来进行定义。
- 在配置文件里面用
- bean 的初始化
- 在配置文件中通过指定init-method属性来完成
- 实现
org.springframwork.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口
- bean 的调用
- 三种方式可以得到bean实例,构造器实例化、静态工厂方法实例化和实例工厂方法实例化,并进行调用。
- bean 的销毁
- 使用配置文件指定的 destroy-method 属性;
- 实现
org.springframwork.bean.factory.DisposeableBean接口.
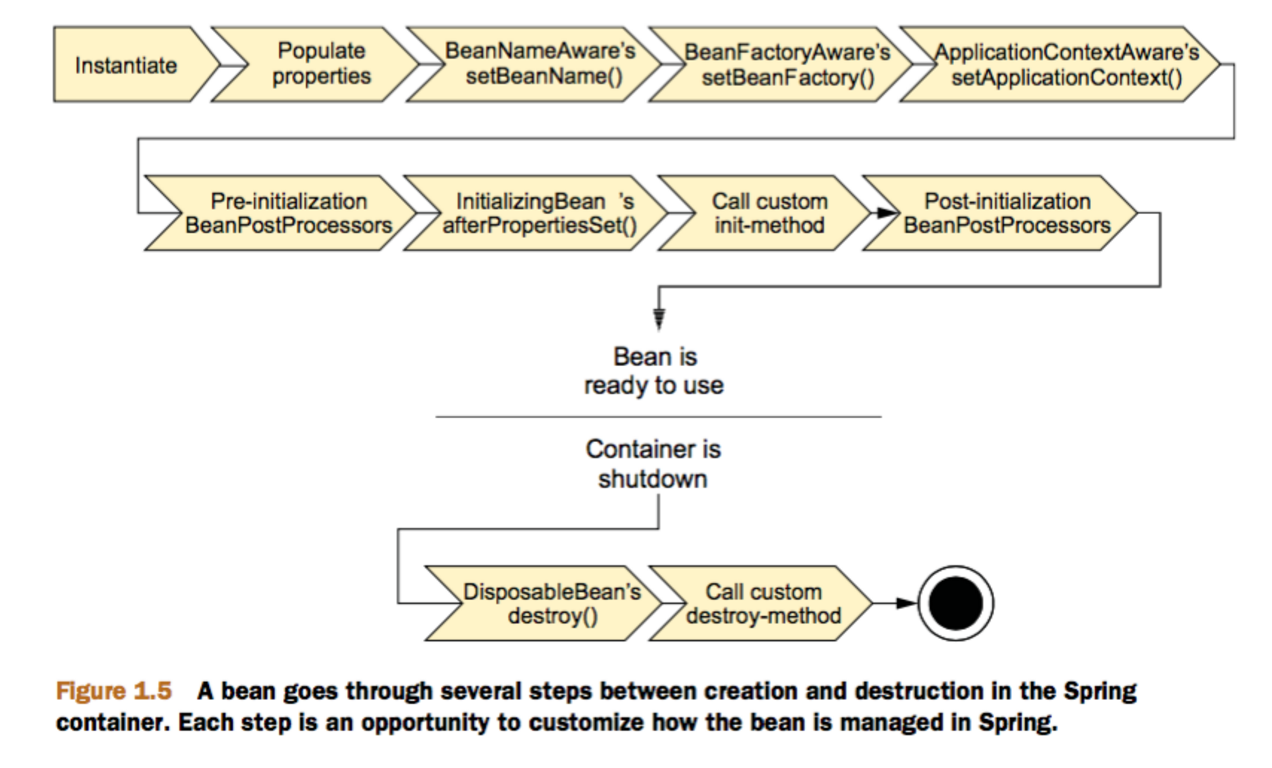
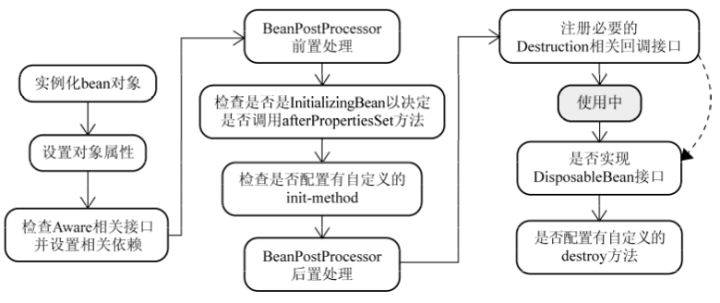
详细的生命周期:
- instantiate bean对象实例化,Bean 容器利用 Java Reflection API 创建一个Bean的实例;
- populate properties 封装属性,如果涉及到一些属性值 利用 set()方法设置一些属性值;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口,调用 setBeanName()方法,传入Bean的名字;
- 如果 Bean 实现 BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware,执行设置工厂 setBeanFactory 或者上下文对象 setApplicationContext,如果实现了其他 *.Aware接口,就调用相应的方法;
- 如果有和加载这个 Bean 的 Spring 容器相关的 BeanPostProcessor 对象,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法,BeanPostProcessor接口提供钩子函数,用来动态扩展修改Bean。(程序自动调用后处理Bean);
- 如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet()方法;
- 如果 Bean 在配置文件中的定义包含 init-method 属性
<bean init-method="init"/>,执行指定的方法; - 如果有和加载这个 Bean的 Spring 容器相关的 BeanPostProcessor 对象,执行postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法;
- 执行业务处理
- 当要销毁 Bean 的时候,如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,执行 destroy() 方法;
- 当要销毁 Bean 的时候,如果 Bean 在配置文件中的定义包含 destroy-method 属性
<bean destroy-method="customerDestroy"/>,执行指定的方法。
Spring 配置 bean 实例化有哪些方式
- 类构造器实例化(默认无参数)
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.spring.UserService"></bean>
- 静态工厂方法实例化(简单工厂模式)
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.spring.StaticBeanFactory" factory-method="getUserService"></bean>
- 实例工厂方法实例化(工厂方法模式)
<bean id="beanFactory" class="com.example.spring.UserBeanFactory"></bean>
<bean id="userService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getUserService"></bean>
Bean 的依赖注入方式
- 基于构造器的依赖注入
public class SimpleMovieLister {
// the SimpleMovieLister has a dependency on a MovieFinder
private MovieFinder movieFinder;
// a constructor so that the Spring container can inject a MovieFinder
public SimpleMovieLister(MovieFinder movieFinder) {
this.movieFinder = movieFinder;
}
// business logic that actually uses the injected MovieFinder is omitted...
}
<beans>
<bean id="beanOne" class="x.y.ThingOne">
<constructor-arg ref="beanTwo"/>
<constructor-arg ref="beanThree"/>
</bean>
<bean id="beanTwo" class="x.y.ThingTwo"/>
<bean id="beanThree" class="x.y.ThingThree"/>
</beans>
<!--Constructor argument type matching-->
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<constructor-arg type="int" value="7500000"/>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="42"/>
</bean>
<!--Constructor argument index-->
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="7500000"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="42"/>
</bean>
<!--Constructor argument name-->
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<constructor-arg name="years" value="7500000"/>
<constructor-arg name="ultimateAnswer" value="42"/>
</bean>
- 基于 Setter 的依赖注入
public class SimpleMovieLister {
// the SimpleMovieLister has a dependency on the MovieFinder
private MovieFinder movieFinder;
// a setter method so that the Spring container can inject a MovieFinder
public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {
this.movieFinder = movieFinder;
}
// business logic that actually uses the injected MovieFinder is omitted...
}
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<!-- setter injection using the nested ref element -->
<property name="beanOne">
<ref bean="anotherExampleBean"/>
</property>
<!-- setter injection using the neater ref attribute -->
<property name="beanTwo" ref="yetAnotherBean"/>
<property name="integerProperty" value="1"/>
</bean>
<bean id="anotherExampleBean" class="examples.AnotherBean"/>
<bean id="yetAnotherBean" class="examples.YetAnotherBean"/>
Spring 注解
将一个类声明为Spring的 bean 的注解
我们一般使用 @Autowired 注解自动装配 bean,要想把类标识成可用于 @Autowired 注解自动装配的 bean 的类,采用以下注解可实现:
- @Component:通用的注解,可标注任意类为 Spring 组件。如果一个Bean不知道属于拿个层,可以使用 @Component 注解标注。
- @Repository:对应持久层即 Dao 层,主要用于数据库相关操作。
- @Service:对应服务层,主要涉及一些复杂的逻辑,需要用到 Dao层。
- @Controller:对应 Spring MVC 控制层,主要用户接受用户请求并调用 Service 层返回数据给前端页面。
@Component 和 @Bean 的区别
- 作用对象不同: @Component 注解作用于类,而 @Bean 注解作用于方法。
- @Component通常是通过类路径扫描来自动侦测以及自动装配到 Spring 容器中(我们可以使用 @ComponentScan 注解定义要扫描的路径从中找出标识了需要装配的类自动装配到 Spring 的 bean 容器中)。@Bean 注解通常是我们在标有该注解的方法中定义产生这个 bean,@Bean 告诉了 Spring 这是某个类的示例,当我需要用它的时候还给我。
- @Bean 注解比 Component 注解的自定义性更强,而且很多地方我们只能通过 @Bean 注解来注册bean。比如当我们引用第三方库中的类需要装配到 Spring容器时,则只能通过 @Bean 来实现。
@Bean 注解的使用示例:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public TransferService transferService() {
return new TransferServiceImpl();
}
}
上面的代码相当于下面的 xml 配置:
<beans>
<bean id="transferService" class="com.acme.TransferServiceImpl"/>
</beans>
这种情况无法通过 @Component 实现:
@Bean
public OneService getService(status) {
case (status) {
when 1:
return new serviceImpl1();
when 2:
return new serviceImpl2();
when 3:
return new serviceImpl3();
}
}
Tagged #spring.